×
Login Form
×
Registration
Profile Informations
Login Datas
or login
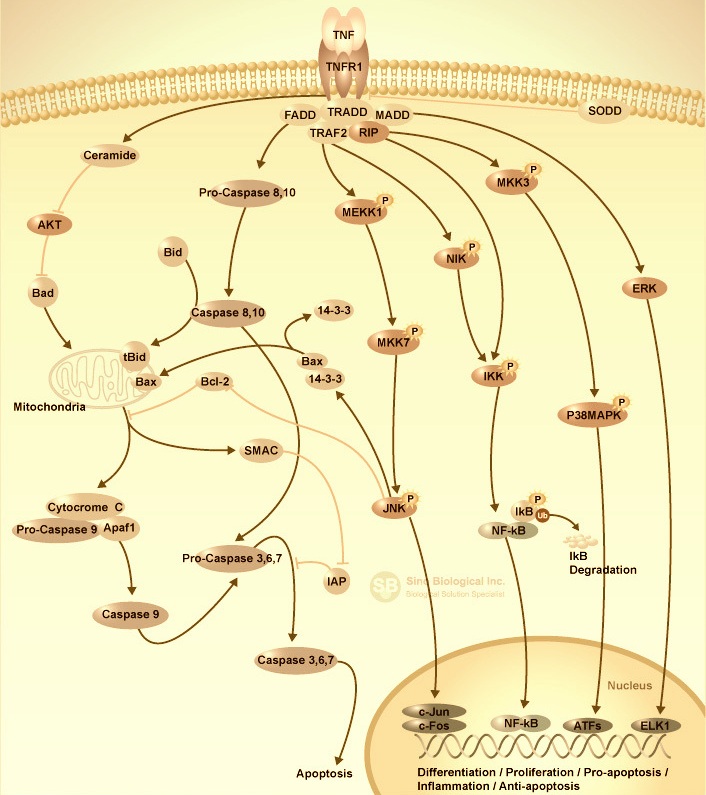
TNF Signaling
The tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily of cytokines activate signaling pathways for cell survival, death, and differentiation. Members of the tumor necrosis factor superfamily act through ligand-mediated trimerization, causing recruitment of several intracellular adaptors to activate multiple signal transduction pathways. Recruitment of death domain (DD) containing adaptors such as Fas associated death domain (FADD) and TNFR associated DD (TRADD) can lead to the activation of a signal transduction pathway that induces apoptosis. While recruitment of TRAF family proteins can lead to the activation of transcription factors such as, NF-kappaB and JNK thereby promoting cell survival and differentiation as well as immune and inflammatory responses.
Inclusion in the tumor necrosis factor ligands and receptors is based on the sequence and structure. The TNF-related ligands are type II transmembrane proteins with an intracellular N-terminus and a ‘TNF homology domain’ (THD) at the extracellular C terminus. The key feature in the receptors is a cysteine-rich domain (CRD) formed of three disulfide bonds surrounding a core motif of CXXCXXC creating an elongated molecule.
Tumor necrosis factor acts via the tumor necrosis factor Receptor (TNFR) and is part of the extrinsic pathway for triggering apoptosis. TNFR is associated with procaspases through adapter proteins (FADD, TRADD, etc.) that can cleave other inactive procaspases and trigger the caspase cascade, irreversibly committing the cell to apoptosis. Research on apoptotic pathways revealed a defect in lysosomal DNA degradation activates macrophages to produce cytokines such as IFNβ and TNF in a Toll-like receptor (TLR)-independent manner. Tumor necrosis factor interacts with tumor cells to trigger cytolysis or cell death. Tumor necrosis factor can also promote inflammatory responses.
TNF Signaling from A to Z
Thanks to Sino Biological for providing the pathways.