×
Login Form
×
Registration
Profile Informations
Login Datas
or login
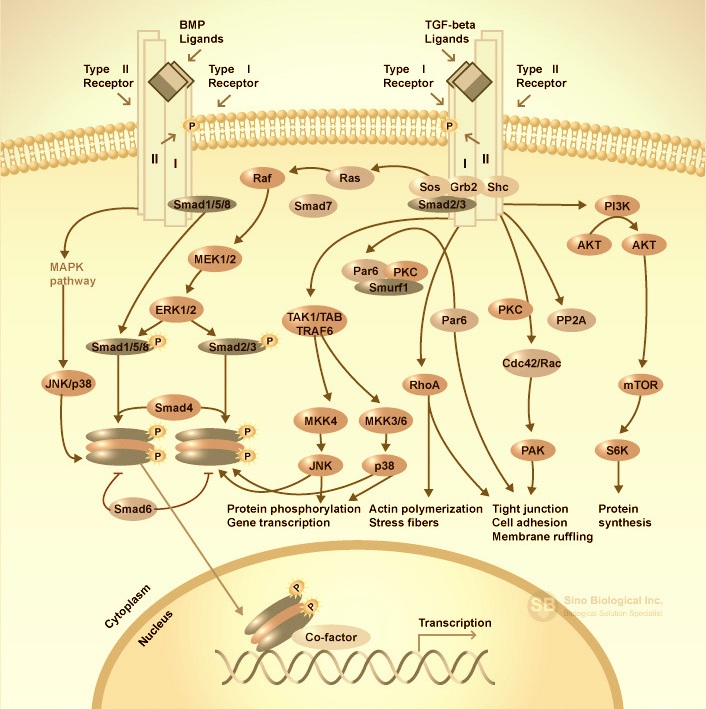
TGF-beta Signaling Pathway
TGF-beta signaling is involved in the regulation of proliferation, differentiation and survival/or apoptosis of many cells, including glioma cells. TGF-beta acts via specific receptors activating multiple intracellular pathways resulting in phosphorylation of receptor-regulated Smad2/3 proteins that associate with the common mediator, Smad4. Such complex translocates to the nucleus, binds to DNA and regulates transcription of many genes. Furthermore, TGF-beta -activated kinase-1 (TAK1) is a component of TGF-beta signaling and activates mitogen-activated protein kinase cascades. Negative regulation of TGF-beta /Smad signaling may occur through the inhibitory Smad6/7. Increased expression of TGF-beta 1-3 correlates with a degree of malignancy of human gliomas. TGF-beta may contribute to tumor pathogenesis by direct support of tumor growth, self-renewal of glioma initiating stem cells and inhibiting of anti-tumor immunity. Inhibitors of TGF-beta signaling reduce viability and invasion of gliomas in animal models and show promises as novel, potential anti-tumor therapeutics.
TGF-beta superfamily of cytokines bind to receptors at the cell surface, and recruit two type I receptors and two type II receptors forming a tetrameric complex. Activated TGF-beta superfamily receptors induce a series of phosphorylation cascade, from receptor phosphorylation to subsequent phosphorylation and activation of downstream signal transducer R-Smads (receptor-activated Smads). Phosphorylated R-Smads form a heteroligomeric (often trimeric) complex with Smad4 (Co-Smad). The Smad complex is imported into the nucleus and regulates the expression of target genes by direct binding to the target gene promoter and/or through the interaction with transcriptional cofactors in a cell-type-specific manner.
TGF-beta Signaling Pathway from A to Z
Thanks to Sino Biological for providing the pathways.