×
Login Form
×
Registrierung
Profile Informationen
Login Daten
oder Einloggen
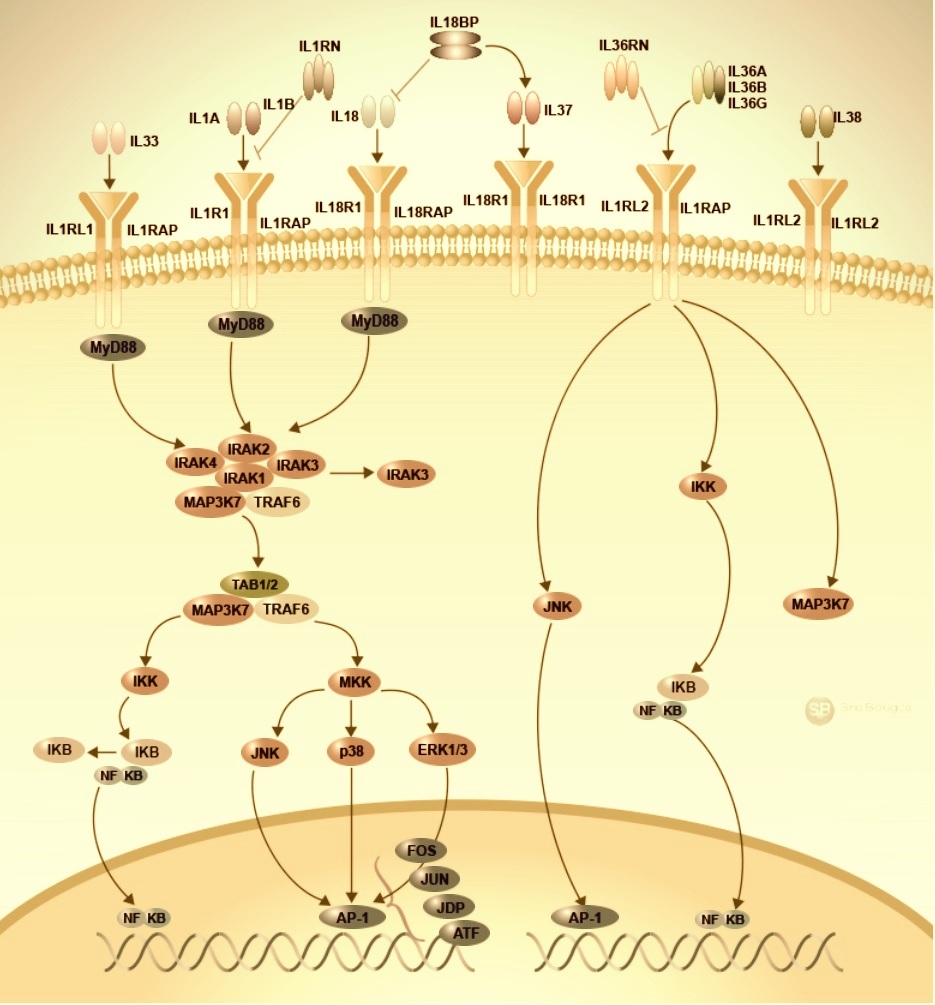
IL1 Siganling Pathway
Many cancers arise at sites of infection and inflammation. Cellular senescence, a permanent state of cell cycle arrest that provides a barrier against tumorigenesis, is accompanied by elevated proinflammatory cytokines such as IL1, IL6, IL8 and TNFα. The IL-1 cytokine family consists of eleven members that play important roles in regulating inflammation. Members include IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-1ra, IL-18, IL-33, IL-36Ra, IL-36 alpha, IL-36 beta, IL-36 gamma, IL-37, and IL-38. While most of these cytokines are biologically active as full-length molecules, activation and secretion of IL-1 beta and IL-18 requires inflammasome/Caspase-1-dependent processing. Other IL-1 family cytokines do not require Caspase-1 cleavage for activation but may undergo some form of protease processing since more potent forms of many of these cytokines can be generated by trimming amino acids at their N-terminal ends. IL-1 family cytokines activate intracellular signaling pathways by binding to a primary receptor subunit, such as IL-1 RI/IL-1 R1, IL-18 R alpha/IL-1 R5, IL-1 Rrp2/IL-1 R6, or ST2/IL-1 R4, which then recruits an accessory receptor to form the active receptor complex. Signaling cascades triggered by IL-1 alpha, IL-1 beta, IL-18, IL-33, IL-36 alpha, IL-36 beta, or IL-36 gamma activate MAPKs and NF-kappa B, leading to the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and secondary mediators of the inflammatory response.In addition, several of these cytokines have been shown to regulate the differentiation and function of T helper cells. Other members of the IL-1 family inhibit inflammation by functioning as antagonists of IL-1 or IL-36 signaling. IL-1ra negatively regulates IL-1 signaling by binding to IL-1 RI and inhibiting its ability to interact with IL-1 alpha and IL-1 beta. Similarly, IL-36Ra binds to IL-1 Rrp2 and inhibits IL-36 signaling. Both IL-37/IL-1F7 and IL-1F10/IL-38 have also been suggested to have anti-inflammatory effects.
IL1 Siganling Pathway from A to Z
Thanks to Sino Biological for providing the pathways.