×
Login Form
×
Registrierung
Profile Informationen
Login Daten
oder Einloggen
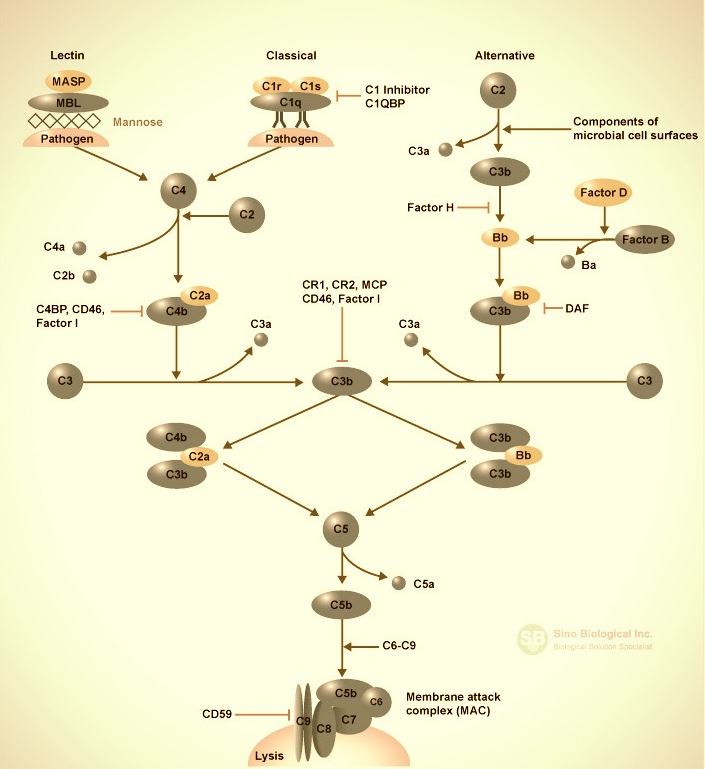
Complement Activation Pathways
The complement system is an enzyme cascade that is a collection of blood and cell surface proteins to help the abilities of antibodies to clear pathogens from an organism. The complement system that comprises 30 different proteins, including serum proteins, serosal proteins, and cell membrane receptors is an important part of the innate immune system. Some complement proteins bind to immunoglobulins or to membrane components of cells. Others are proenzymes that, when activated, cleave one or more other complement proteins and initiate an amplifying cascade of further cleavages. The end-result of this cascade is massive amplification of the response and activation of the cell-killing membrane attack complex. The complement system has four major function, including lysis of infectious organisms, activation of inflammation, opsonization and immune clearance.
There are three different complement pathways, the classical complement pathway, the alternative complement pathway, and the mannose-binding lectin pathway. The classic complement pathway is triggered when antibody-antigen complex interact with C1-complex, which consists of C1q, two molecules of C1r, and two molecules of C1s. The C1-complex cleaves C2 and C4, which then form C3 convertase (C4b2a). C3 is then cleaved by the C3 convertase, and forms C5 convertase in association with C4b and C2a. The generation of C5 convertase is the end of the classical pathway. The lectin pathway is very similar to the classical pathway. It is stimulated when the mannose-binding lectin (MBL) binds to mannose residues on the pathogen surface. The MBL-associated serine proteases, MASP-1, and MASP-2, are activated and cleave C4 and C2, which then form the C3 convertase as in the classical pathway. The alternative complement pathway begins with the activation of C3 and requires factor B and factor D. All three pathways merge at C3, which is then converted into C3a and C3b.
Complement Activation Pathways from A to Z
| SINGLE COMPONENTS | PRODUCTS |
|---|---|
| AKT | search result |
| ERK | search result |
| GRB2 | search result |
| IL15 | search result; Category: IL15 |
| IL13RA1 | search result; Category: IL13RA1 |
| IL2 | search result; Category: IL2 |
| IL21 | search result; Category: IL21 |
| IL21R | search result; Category: IL21R |
| IL2R | search result; Category: IL2R |
| IL2RB | search result; Category: IL2RB |
| IL2RG | search result; Category: IL2RG |
| IL4 | search result; Category: IL4 |
| IL4R | search result; Category: IL4R |
| IL7 | search result; Category: IL7 |
| IL7R | search result; Category: IL7R |
| IL9 | search result; Category: IL9 |
| IL9R | search result; Category: IL9R |
| JAK | search result |
| JAK1 | search result |
| JAK3 | search result |
| MEK | search result |
| mTOR | search result |
| P13K | search result |
| PIAS | search result |
| PTPase | search result |
| Raf | search result |
| Ras | search result |
| Shc | search result |
| STAT | search result |
| TYK2 | search result |
Thanks to Sino Biological for providing the pathways.